2024
Leveraging Unpaired Data for the Creation of Controllable Digital Humans
Realistic Digital Human Characters: Challenges, Models and Algorithms
Modelling Dynamic 3D Human-Object Interactions: From Capture to Synthesis
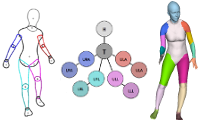
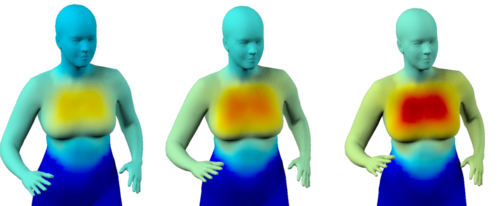
Self- and Interpersonal Contact in 3D Human Mesh Reconstruction
Natural Language Control for 3D Human Motion Synthesis
2022
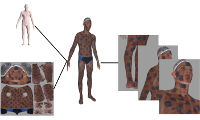
Reconstructing Expressive 3D Humans from RGB Images
2019
Towards Geometric Understanding of Motion
The motion of the world is inherently dependent on the spatial structure of the world and its geometry. Therefore, classical optical flow methods try to model this geometry to solve for the motion. However, recent deep learning methods take a completely different approach. They try to predict optical flow by learning from labelled data. Although deep networks have shown state-of-the-art performance on classification problems in computer vision, they have not been as effective in solving optical flow. The key reason is that deep learning methods do not explicitly model the structure of the world in a neural network, and instead expect the network to learn about the structure from data. We hypothesize that it is difficult for a network to learn about motion without any constraint on the structure of the world. Therefore, we explore several approaches to explicitly model the geometry of the world and its spatial structure in deep neural networks.
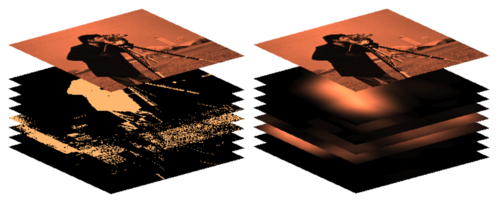
The spatial structure in images can be captured by representing it at multiple scales. To represent multiple scales of images in deep neural nets, we introduce a Spatial Pyramid Network (SpyNet). Such a network can leverage global information for estimating large motions and local information for estimating small motions. We show that SpyNet significantly improves over previous optical flow networks while also being the smallest and fastest neural network for motion estimation. SPyNet achieves a 97% reduction in model parameters over previous methods and is more accurate.
The spatial structure of the world extends to people and their motion. Humans have a very well-defined structure, and this information is useful in estimating optical flow for humans. To leverage this information, we create a synthetic dataset for human optical flow using a statistical human body model and motion capture sequences. We use this dataset to train deep networks and see significant improvement in the ability of the networks to estimate human optical flow.
The structure and geometry of the world affects the motion. Therefore, learning about the structure of the scene together with the motion can benefit both problems. To facilitate this, we introduce Competitive Collaboration, where several neural networks are constrained by geometry and can jointly learn about structure and motion in the scene without any labels. To this end, we show that jointly learning single view depth prediction, camera motion, optical flow and motion segmentation using Competitive Collaboration achieves state-of-the-art results among unsupervised approaches.
Our findings provide support for our hypothesis that explicit constraints on structure and geometry of the world lead to better methods for motion estimation.
2018
Model-based Optical Flow: Layers, Learning, and Geometry
Combining Data-Driven 2D and 3D Human Appearance Models
2017
Human Shape Estimation using Statistical Body Models
Learning Inference Models for Computer Vision
Capturing Hand-Object Interaction and Reconstruction of Manipulated Objects
2016
Non-parametric Models for Structured Data and Applications to Human Bodies and Natural Scenes
2015
Shape Models of the Human Body for Distributed Inference
From Scans to Models: Registration of 3D Human Shapes Exploiting Texture Information
Long Range Motion Estimation and Applications
2014
Modeling the Human Body in 3D: Data Registration and Human Shape Representation
2013
Statistics on Manifolds with Applications to Modeling Shape Deformations
Probabilistic Models for 3D Urban Scene Understanding from Movable Platforms
2012
Virtual Human Bodies with Clothing and Hair: From Images to Animation
From Pixels to Layers: Joint Motion Estimation and Segmentation
1992
Robust Incremental Optical Flow