7 results
(View BibTeX file of all listed publications)
2021
Scientific Report 2016 - 2021
2021 (mpi_year_book)
This report presents research done at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems from January2016 to November 2021. It is our fourth report since the founding of the institute in 2011. Dueto the fact that the upcoming evaluation is an extended one, the report covers a longer reportingperiod.This scientific report is organized as follows: we begin with an overview of the institute, includingan outline of its structure, an introduction of our latest research departments, and a presentationof our main collaborative initiatives and activities (Chapter1). The central part of the scientificreport consists of chapters on the research conducted by the institute’s departments (Chapters2to6) and its independent research groups (Chapters7 to24), as well as the work of the institute’scentral scientific facilities (Chapter25). For entities founded after January 2016, the respectivereport sections cover work done from the date of the establishment of the department, group, orfacility. These chapters are followed by a summary of selected outreach activities and scientificevents hosted by the institute (Chapter26). The scientific publications of the featured departmentsand research groups published during the 6-year review period complete this scientific report.
Scientific Report 2016 - 2018
2019 (mpi_year_book)
This report presents research done at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems from
January 2016 to December 2018. It is our third report since the founding of the institute in 2011.
This status report is organized as follows: we begin with an overview of the institute, including
its organizational structure (Chapter 1). The central part of the scientific report consists of chapters
on the research conducted by the institute’s departments (Chapters 2 to 5) and its independent
research groups (Chapters 6 to 18), as well as the work of the institute’s central scientific facilities
(Chapter 19). For entities founded after January 2016, the respective report sections cover work
done from the date of the establishment of the department, group, or facility.
2014
Learning People Detectors for Tracking in Crowded Scenes.
Tang, S., Andriluka, M., Milan, A., Schindler, K., Roth, S., Schiele, B.
2014, Scene Understanding Workshop (SUNw, CVPR workshop) (unpublished)
2013
A Study of X-Ray Image Perception for Pneumoconiosis Detection
IIIT-Hyderabad, Hyderabad, India, January 2013 (mastersthesis)
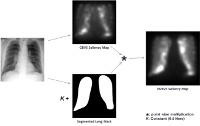
Pneumoconiosis is an occupational lung disease caused by the inhalation of industrial dust. Despite the increasing safety measures and better work place environments, pneumoconiosis is deemed to be the most common occupational disease in the developing countries like India and China. Screening and assessment of this disease is done through radiological observation of chest x-rays. Several studies have shown the significant inter and intra reader observer variation in the diagnosis of this disease, showing the complexity of the task and importance of the expertise in diagnosis.
The present study is aimed at understanding the perceptual and cognitive factors affecting the reading of chest x-rays of pneumoconiosis patients. Understanding these factors helps in developing better image acquisition systems, better training regimen for radiologists and development of better computer aided diagnostic (CAD) systems. We used an eye tracking experiment to study the various factors affecting the assessment of this diffused lung disease. Specifically, we aimed at understanding the role of expertize, contralateral symmetric (CS) information present in chest x-rays on the diagnosis and the eye movements of the observers. We also studied the inter and intra observer fixation consistency along with the role of anatomical and bottom up saliency features in attracting the gaze of observers of different expertize levels, to get better insights into the effect of bottom up and top down visual saliency on the eye movements of observers.
The experiment is conducted in a room dedicated to eye tracking experiments. Participants consisting of novices (3), medical students (12), residents (4) and staff radiologists (4) were presented with good quality PA chest X-rays, and were asked to give profusion ratings for each of the 6 lung zones. Image set consisting of 17 normal full chest x-rays and 16 single lung images are shown to the participants in random order. Time of the diagnosis and the eye movements are also recorded using a remote head free eye tracker.
Results indicated that Expertise and CS play important roles in the diagnosis of pneumoconiosis. Novices and medical students are slow and inefficient whereas, residents and staff are quick and efficient. A key finding of our study is that the presence of CS information alone does not help improve diagnosis as much as learning how to use the information. This learning appears to be gained from focused training and years of experience. Hence, good training for radiologists and careful observation of each lung zone may improve the quality of diagnostic results. For residents, the eye scanning strategies play an important role in using the CS information present in chest radiographs; however, in staff radiologists, peripheral vision or higher-level cognitive processes seems to play role in using the CS information.
There is a reasonably good inter and intra observer fixation consistency suggesting the use of similar viewing strategies. Experience is helping the observers to develop new visual strategies based on the image content so that they can quickly and efficiently assess the disease level. First few fixations seem to be playing an important role in choosing the visual strategy, appropriate for the given image.
Both inter-rib and rib regions are given equal importance by the observers. Despite reading of chest x-rays being highly task dependent, bottom up saliency is shown to have played an important role in attracting the fixations of the observers. This role of bottom up saliency seems to be more in lower expertize groups compared to that of higher expertize groups. Both bottom up and top down influence of visual fixations seems to change with time. The relative role of top down and bottom up influences of visual attention is still not completely understood and it remains the part of future work.
Based on our experimental results, we have developed an extended saliency model by combining the bottom up saliency and the saliency of lung regions in a chest x-ray. This new saliency model performed significantly better than bottom-up saliency in predicting the gaze of the observers in our experiment. Even though, the model is a simple combination of bottom-up saliency maps and segmented lung masks, this demonstrates that even basic models using simple image features can predict the fixations of the observers to a good accuracy.
Experimental analysis suggested that the factors affecting the reading of chest x-rays of pneumoconiosis are complex and varied. A good understanding of these factors definitely helps in the development of better radiological screening of pneumoconiosis through improved training and also through the use of improved CAD tools. The presented work is an attempt to get insights into what these factors are and how they modify the behavior of the observers.
2012
An Analysis of Successful Approaches to Human Pose Estimation
An Analysis of Successful Approaches to Human Pose Estimation, University of Augsburg, University of Augsburg, May 2012 (mastersthesis)
The field of Human Pose Estimation is developing fast and lately leaped forward
with the release of the Kinect system. That system reaches a very good perfor-
mance for pose estimation using 3D scene information, however pose estimation
from 2D color images is not solved reliably yet. There is a vast amount of pub-
lications trying to reach this aim, but no compilation of important methods and
solution strategies. The aim of this thesis is to fill this gap: it gives an introductory
overview over important techniques by analyzing four current (2012) publications
in detail. They are chosen such, that during their analysis many frequently used
techniques for Human Pose Estimation can be explained. The thesis includes two
introductory chapters with a definition of Human Pose Estimation and exploration
of the main difficulties, as well as a detailed explanation of frequently used methods.
A final chapter presents some ideas on how parts of the analyzed approaches can
be recombined and shows some open questions that can be tackled in future work.
The thesis is therefore a good entry point to the field of Human Pose Estimation
and enables the reader to get an impression of the current state-of-the-art.